This article was recently published by Components in Electronics, CIE, and written by TT Electronics' Business Development Engineer, Sergey Komarov. He discusses next-gen optical encoders that uniquely monitor the health of their system environment.
Industry 4.0 starts with smart factories utilising smart sensing technologies, where digitised intelligent platforms enable best-in-class manufacturing processes. Data-driven manufacturing relies on smart sensors which enable manufacturing processes and predictive maintenance with minimal downtime, maximum efficiency and sustainable throughput. This precise level of control, data collection and processing is guaranteed by a new generation of highly integrated, multi-functional smart optical sensors.
An optical sensor is a critical part of the sensory neural system of industrial automation and robotics applications. Smart optical sensors were developed in response to modern lifestyle changes which emphasise mobility, energy efficiency to prolong battery life, ambient light immunity to full sunlight, programmability to detect surfaces with different reflectivity, temperature compensation, and aging. Next-generation sensors go even further, offering breakthrough features that accelerate time to market by reducing engineering cost and effort. Illustrated by TT Electronics’ FlexSense optical encoder sensor, this next-generation device is capable not only of detecting motion and position as its primary function, but it also monitors its environment to diagnose early signs of potential system failure. Portfolio complexity is reduced with a “one-size-fits-many” solution, increasing manufacturing throughput and cost efficiency.
Most encoders detect rotation or linear motion – information which is then fed back into the computer for measuring and controlling velocity or position. The main applications are motor control, speed and direction feedback, robotics, and numerical control CNC machines. Traditional encoder systems utilise sensors that have fixed photo-arrays designed for a specific code-wheel configuration.
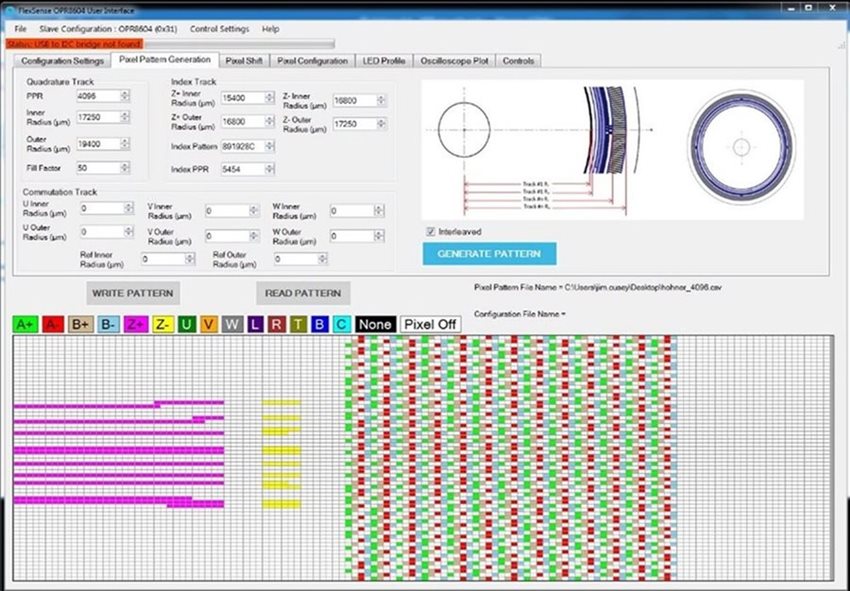
By contrast, the high-resolution pixel array on an optimised sensor such as FlexSense is user-programmable, enabling quick customisation in seconds for a diverse size of code wheels radii from 10 to 40mm and multiple pulses per revolution. This optimised encoder includes 2 quadrature tracks which can be programmed to have analog or digital outputs and 1 index track. It is compatible with code-disk resolutions of up to 1,200 lines per inch, or 4,096 PPR at a 15mm optical radius with on-chip quad-track interpolation (2x, 4x, 8x) and division (power of 2 up to 2,048). Quad-track output characteristics at native frequency up to 400kHz with a total harmonic distortion of less than 1.0% on analog output, transient noise less than or equal to 1.0% of signal amplitude on analog output at 40mW/cm2, angular position accuracy +- part in 100K, or about 12 arc-seconds at 1,500 PPR, on digital outputs. It uses single-supply 3.3V+-10% operation. All these features are integrated in a compact 32-pin 5mm x 5 mm x 0.65mm opto QFN surface mount package with wide ambient operating temperature of -40C to +125C.
The three main performance characteristics of optical encoders are: Resolution, Accuracy, and Repeatability.
Resolution is the number of bits of words dictated by the number of positions to be measured. If a system needed to measure travel of a lead screw in 0.01 mm increments over 25cm, then an encoder with a resolution of 25,000 words would be required. Industrial encoders can provide direct readings from the code disk well above 16,384 words (16 bits).
Accuracy refers to the precision of the output signal relative to shaft position. In typical industrial absolute single-turn encoders, the output signal is within +11/2 LSB of the ideal for resolution up to 13 bits. Accuracies of +-1 are achieved for higher resolutions. For multi-turn encoders, the value of +-1 count of the input (fine) encoder, translating to ta nominal accuracy of =-40 arc-seconds for a 16 bit encoder.
Repeatability is the ability of the encoder to read the same word each time the shaft is in the same position. Repeatability has no relation to accuracy. It is 10x better than accuracy, but can be affected by other system components (couplings, gears, etc.) which can have mechanical hysteresis.
Optimised encoders read quadrature signals A+, A-, B+, B-. By properly decoding and counting these signals, the direction of motion, speed, and relative position of the encoder can be determined. The direction of the rotation can be detected by monitoring the relative phase of both signals. For example, if Channel A leads Channel B, then CCW movement could be indicated. Conversely, if Channel B leads Channel A, CW rotation could be indicated. The shorter the signal period, the smaller the measuring step.
Adopting smart factory technologies utilising smart sensors is just the beginning of modern industrial advancement. Industry 4.0 demands the overall integration of intelligent core operations such as procurement, finance, sales and marketing. This creates a dynamic digital ecosystem that enables people, machines, and systems to work together in optimum techno-symbiosis. By utilising smart encoder options such as FlexSense sensors paired with data analytics and sophisticated AI strategy, industrial operations can gain access to the intelligence needed to transform and sustain business value.
The Del Mar Electronics and Manufacturing show is an electronic show which showcases electronic components and subassemblies in a focused event which offers Industry Programs & High Tech Presentations By Leading Edge Companies.
Significant contract will see TT’s Fairford UK facility provide mission-critical cable harness assemblies for global defence programmes.
Significant funding package awarded to support advancement of technology roadmap for a more sustainable aviation sector.